Classification of Solids
In solids, the arrangement of energy levels leads to the formation of valence band (filled with electrons) and conduction band (where electrons can move freely). The energy band gap (𝐸g) between them determines whether a solid is a conductor, semiconductor, or insulator.
- Conductors
In conductors, the valence band and conduction band overlap, which means there is no band gap (𝐸𝑔≈0). As a result, electrons can move freely from the valence band to the conduction band, leading to very high electrical conductivity. Typical examples of conductors include metals such as copper (Cu), aluminum (Al), and silver (Ag).
- Semiconductors Semiconductors have a small band gap (𝐸𝑔≈0.1–3eV). At room temperature, some electrons gain enough thermal energy to cross from the valence band into the conduction band. As a result, their electrical conductivity increases with temperature. Common examples of semiconductors include silicon ( \(E_g=1.1eV\)) and germanium ( \(E_g=0.7eV\)).
- Insulators Insulators have a large band gap (𝐸𝑔>3eV), which makes it very difficult for electrons in the valence band to gain enough energy to move into the conduction band. As a result, they have extremely low electrical conductivity under normal conditions. Typical examples of insulators include diamond ( \(E_g=5.5eV \)) and glass.
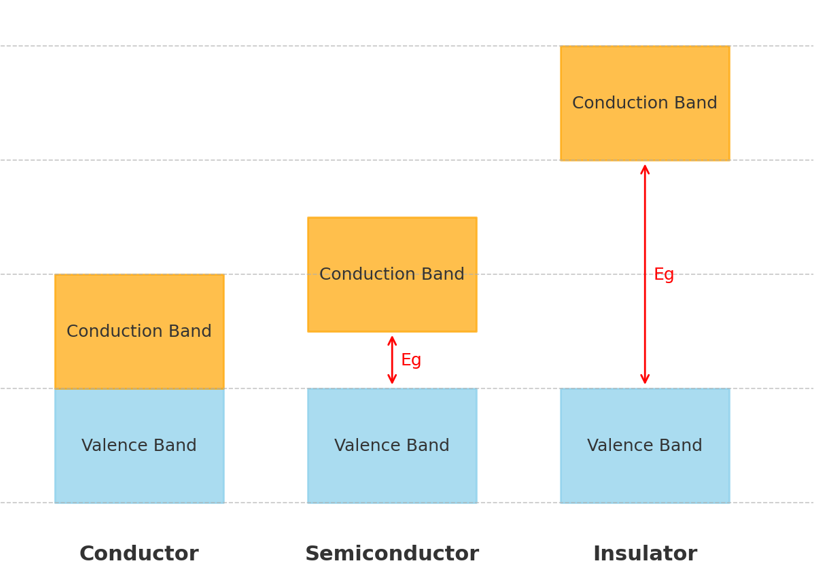
Energy bandgap of solids of conductors, semiconductors and insulators
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
-
Which of the following statements is true for conductors?
- a) They have a large energy band gap
- b) Their valence band is completely empty
- c) Their valence and conduction bands overlap
- d) They have a band gap of about 5 eV
Answer
c) Their valence and conduction bands overlap
-
The energy band gap of silicon at room temperature is approximately:
- a) 0 eV
- b) 1.1 eV
- c) 3.0 eV
- d) 5.5 eV
Answer
b) 1.1 eV
-
In insulators, the energy band gap is typically:
- a) Very small (≈ 0 eV)
- b) Around 0.1 eV
- c) Greater than 3 eV
- d) Overlapping bands
Answer
c) Greater than 3 eV
-
Which solid has overlapping valence and conduction bands?
- a) Diamond
- b) Copper
- c) Silicon
- d) Germanium
Answer
b) Copper
-
Which correctly represents the increasing order of energy band gap?
- a) Insulator < Semiconductor < Conductor
- b) Conductor < Semiconductor < Insulator
- c) Semiconductor < Conductor < Insulator
- d) Conductor < Insulator < Semiconductor
Answer
b) Conductor < Semiconductor < Insulator