Formation of energy bands & Origin band gap
Quick Exam Notes
- Energy bands form due to overlapping of atomic orbitals when atoms are closely packed in solids.
- Valence Band (VB): Highest range of energies occupied by electrons at 0 K.
- Conduction Band (CB): Higher energy band where electrons are free to move.
- Band Gap (Eg): Energy difference between CB and VB → \( E_g = E_c - E_v \).
- Classification: Conductors (no gap), Semiconductors (small gap), Insulators (large gap).
- In an isolated atom, electrons occupy specific energy levels. When many atoms come close together to form a solid, their outer (valence) electrons start interacting. Because of this interaction, the discrete energy levels of individual atoms split into many closely spaced levels shown in Fig.1.
- Due to the Pauli Exclusion Principle, electrons in overlapping orbitals cannot have the same energy. This causes the discrete energy levels of individual atoms to split into multiple closely spaced levels.
- Since the number of atoms is huge, these levels lie so close that they appear as a continuous band of energies, called an energy band.
- Valence Band: formed from the outermost electrons at absolute zero K.
- Conduction Band: higher energy band where electrons can move freely and conduct electricity.
- The energy gap (band gap) between these two bands decides whether the material is a conductor, semiconductor, or insulator.
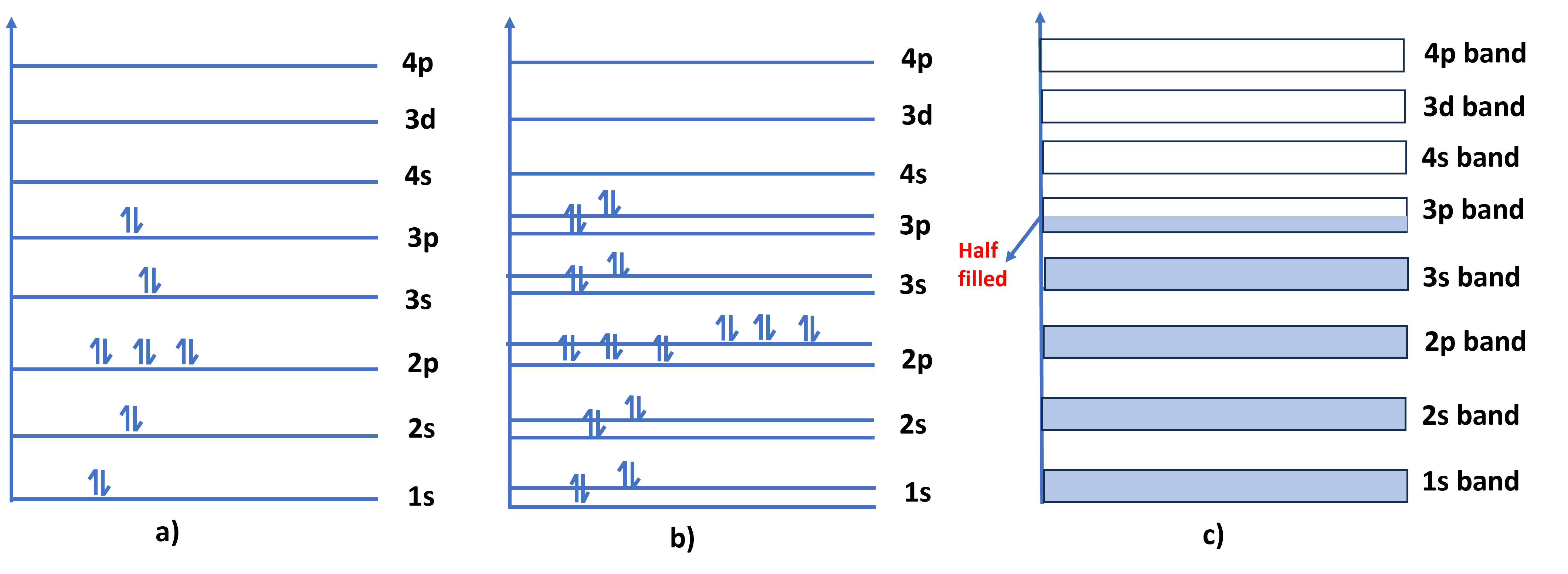
Figure 1. a) Electron configuration of a single silicon atom b) pair of silicon atoms considered together and c) Band formation in a mass of silicon with N atoms.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
-
The formation of energy bands in solids is due to:
- a) Motion of free electrons
- b) Overlapping of atomic orbitals in closely packed atoms
- c) Scattering of electrons
- d) Presence of impurities
Answer
b) Overlapping of atomic orbitals in closely packed atoms
-
When isolated atoms come close to form a solid, their discrete energy levels:
- a) Remain unchanged
- b) Split into a large number of closely spaced levels forming bands
- c) Merge into a single energy level
- d) Disappear completely
Answer
b) Split into a large number of closely spaced levels forming bands
-
The energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band is called:
- a) Fermi energy
- b) Band gap
- c) Potential energy
- d) Forbidden energy gap
Answer
d) Forbidden energy gap
-
In conductors, the valence band and conduction band:
- a) Are separated by a large energy gap
- b) Overlap each other
- c) Are far apart
- d) Are the same
Answer
b) Overlap each other
-
The band gap is maximum in:
- a) Conductors
- b) Semiconductors
- c) Insulators
- d) Metals
Answer
c) Insulators