Sol-Gel (Bottom-Up) Method
The sol–gel process represents the chemical transformation of a system from a liquid “sol” (mostly a colloidal suspension of particles) into a gelatinous network “gel” phase with subsequent post-treatment and transition into solid oxide material. This sol-gel process is well adapted for composite nanopowder (NP) synthesis, and oxide NPs Certain experimental conditions are required in the Sol-Gel method such as specific reaction time, temperature, solution concentration, stoichimetry. Figure 1 shows the step by step process to synthesize nanomaterials.
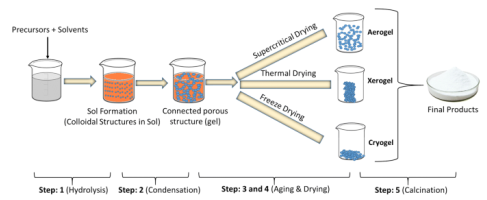
Figure 1. Process flow of sol-gel method
- We start with reactants of suitable stoichiometry. The solution is mixed well in a magnetic stirrer.
- For a uniform mixture the stirring process may take few hours.
- The solution is kept for ageing, inorder to deposit thin film by dip or spin coating method.
- In order to synthesize nanopowders, suitable combustion source is added to the solution. Usually Glycin, Urea are used.
- The solution is heated at suitable temperature in order to get nano powder ashes. The ashes are collected, grinded in mortar and pestle in order to get the desired nanopowder
- Typical sizes of particles produced by this method are 5-30 nm.
Advantages
- Less time consuming as compared to ball milling method
- Uniform size distribution
- Doping is easy
- Low temperature densification
Disadvantages
- Toxic gasses evolves in some reaction
- Cost of raw materials can be high
- Chances of contamination is more