Chemical Vapor Deposition (Top-Down) Method
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a chemical process is a whereby a thin solid film is deposited onto a substrate through chemical reactions of the gaseous species. For structural component applications, the deposition typically takes place at a temperature of around 1000oC.
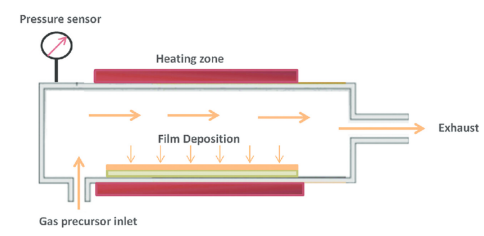
Figure 1. Chemical vapour deposition method
Figure 1 gives a typical example of a CVD system, where reactant gases, normally called precursor gases of CH3SiCl3 and H2, are delivered into a reaction chamber at a suitably determined temperature. As they pass through the reactor these gases come into contact with a heated substrate; they then react and form a solid SiC layer deposited onto the surface of a substrate. Usually, an inert gas, such as Ar, is used as a diluent gas. The depositing temperature and pressure are the critical parameters in this process. After the reactions, the exhaust gases containing HCl species are trapped by NaOH and then condensed by liquid N2 trap before being released into the atmosphere.
Advantages
- Versatile- any element or compound can be deposited
- High purity can be obtained
- High density – nearly 100% of the theoretical value
- Economical in production, since many parts can be coated at the same time
Disadvantages
- High deposition temperatures (usually greater than 600oc)
- Restrictions on the kind of substrates that can be coated.
- Chances of contamination is more
- Chemical and safety hazards caused by the use of toxic, corrosive, explosive precursor.